Glaucoma is not a single disease process. It is a group of eye disorders characterized by a progressive
death of the optic nerve head which is the link from the eyes to the brain in structure and function. This
results to a characteristic appearance of the optic disc and a specific pattern of visual field defect.
Intraocular pressure (IOP) is the most common but not the only risk factor. The cause of glaucoma is still
not clearly understood and it remains an enigma.
STATISTICS
According to World Health Organization (WHO)
Glaucoma is the second most common cause of blindness worldwide.
Accounts for 8% of blindness among the 39 million people who are blind
In Africa, glaucoma accounts for 15% of blindness
Blindness from glaucoma is irreversible.
FACTS TO NOTE
Vision damage due to glaucoma is permanent/irreversible
Vision loss in glaucoma is usually gradual starting from the peripheral vision, eventually the
individual gets tunnel vision and then total loss of vision.
Early detection is key to management
It may lead to total blindness if not properly managed
Most victims are not aware of the condition
Glaucoma is not cured but managed
WHAT IT IS NOT
It is not an attack from enemies
It is not a familial curse
It is not a punishment for sins
It is not a result of long -term use of glasses
It is not associated with social status
RISK FACTORS
Raised intra ocular pressure (IOP)
Age: it can occur at any age but risk increases with increasing age
Heredity
Race – blacks are more susceptible compared to Caucasians
Refractive errors especially high myopia
Trauma
Some eye diseases e.g. uveitis, Diabetic retinopathy
Smoking
Prolonged use of steroids
Some health conditions like diabetes and hypertension increases ones risk
TYPES
- Primary open angle glaucoma (POAG)
- Normal tension glaucoma (NTG)
- Ocular hypertension (OHT)
- Primary angle closure glaucoma (PACG)
- Secondary glaucoma
- Congenital glaucoma
SYMPTOMS IN PRIMARY OPEN ANGLE GLAUCOMA (POAG)
It’s a sneak thief of sight
No symptoms noticed until significant vision loss has occurred.
This accounts for 90% of glaucomas
SYMPTOMS IN PRIMARY ANGLE CLOSURE GLAUCOMA (PACG)
- Hazy or blurred vision
- Appearance of rainbow coloured circles / halos around bright light
- Severe eye and head pain
- Nausea or vomiting accompanying severe eye pain
- Sudden sight loss
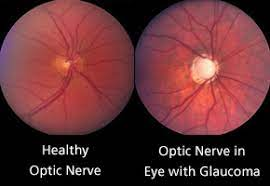
VISION LOSS IN GLAUCOMA

Early detection is the main stay of preventing visual loss in glaucoma .
Sensitization on glaucoma awareness: Annually a week is set aside world -wide for sensitization
and glaucoma awareness. This is termed the World glaucoma week and comes up on the 2 nd
week of March each year.
Screening of first- degree family members is very important especially if there is a positive family
history of glaucoma
MANAGEMENT
Glaucoma has no cured but is managed. The goal of management is to preserve remaining vision and
not to restore vision which may have been lost.
Routine eye check, more frequent if pre – disposed
Routine IOP check
Annual visual field check
Compliance with medications and follow up visits for people who have been diagnosed
Trabeculectomy (surgery) when medications are not giving desired control
Do not allow glaucoma steal your vision, go for comprehensive eye examination yearly. “An eye check a
year, keeps blindness away”
